In this issue
- Are we in an infodemic?
- How did we get here?
- Respecting and promoting science: what it means for the Canadian arthritis community
- Why arthritis research is important for us
- ACE responds to the infodemic
- Lifestyle Tips from our Arthritis at Home Experts
- Staying Nourished During the Pandemic
JointHealth™ insight Published August 2020
 Over the past five months, Canadians have shared their stories and concerns about their experience watching television, listening to talk radio or on social media platforms reading posts calling COVID-19 a “political hoax” or that the virus has been created in a government laboratory with no consumer warning or label on these reports. The International Fact-checking Network has called COVID–19 “the biggest challenge fact-checkers have ever faced.” In July 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) hosted the first “infodemiology” conference to study the infodemic of misinformation and disinformation around the coronavirus.
Over the past five months, Canadians have shared their stories and concerns about their experience watching television, listening to talk radio or on social media platforms reading posts calling COVID-19 a “political hoax” or that the virus has been created in a government laboratory with no consumer warning or label on these reports. The International Fact-checking Network has called COVID–19 “the biggest challenge fact-checkers have ever faced.” In July 2020, the World Health Organization (WHO) hosted the first “infodemiology” conference to study the infodemic of misinformation and disinformation around the coronavirus.
In this issue of JointHealth™ insight, Arthritis Consumer Experts (ACE) covers what you need to know about the ‘infodemic’, how we got here and what it means for arthritis patients and researchers. As an additional bonus section, we also provide some fun and helpful lifestyle tips shared by experts on our Arthritis At Home program. Afterall, even during a pandemic, people living with arthritis want to make the most of their summer and keep their joints as happy and healthy as possible! According to WHO, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, the phenomenon of an “infodemic” has escalated to a level that requires a coordinated response. WHO defines an infodemic as “an overabundance of information, some accurate and some not—that makes it hard for people to find trustworthy sources and reliable guidance when they need it.” Even when people have access to high-quality information, misinformation continues to spread further and faster and adds complexity to a public health emergency response.
According to WHO, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, the phenomenon of an “infodemic” has escalated to a level that requires a coordinated response. WHO defines an infodemic as “an overabundance of information, some accurate and some not—that makes it hard for people to find trustworthy sources and reliable guidance when they need it.” Even when people have access to high-quality information, misinformation continues to spread further and faster and adds complexity to a public health emergency response.

How did we get here?
What we have learned over the past five months is that the traditional media and, even more importantly, high-powered social media have accelerated the spread of lies and the political polarization that motivates people to believe misinformation. Experts are concerned that unless the public health sphere can effectively counter misinformation, not even an effective vaccine may be enough to end the pandemic.
While fake news is anything but new, the difference is the infodemic can make people sick and even kill them if they don’t understand what precautions to take.
Beyond its effect on individuals, the infodemic erodes trust in science and government leadership at the moment when that trust is most needed. A study by the Reuters Institute found 39% of English-language misinformation assessed between January and March included false claims about the actions or policies of authorities.
The infodemic has spread nearly as widely as the pandemic itself in North America. Based on an online survey by Ryerson University researchers, misinformation about the COVID-19 pandemic is reaching a majority of Canadians who use social media and popular apps. Nearly 7 in 10 Canadians who responded to the survey said they had personally encountered misinformation about the global health crisis on social media platforms or on popular aggregator websites like Reddit.
In the US, 38% of Americans surveyed by Pew in June said that compared to the first couple of weeks of the pandemic, they found it harder to identify what was true and what was false about the virus.
An evolving outbreak: Misinformation and disinformation have always been a destabilizing feature of infectious disease outbreaks. But several factors have made the situation worse with COVID-19.
COVID-19 is new, and as scientists have learned more about the virus, they’ve had to change recommendations based on new evidence and science. That’s how science works but for people who are distrustful of health authorities, an expert changing a guideline or recommendation in a matter of days or weeks just confirms their bias and unfounded suspicions about public health recommendations.
The use of masks is an excellent example. Back in February, North American health authorities were not recommending wearing masks; by May, based on real-world evidence from countries who effectively flattened the curve, our authorities began recommending the use of masks in public places where physical distancing was difficult to maintain. Today, people are still arguing about wearing masks—a tiny infringement of personal freedoms that represents one of the few hopes of easing the spread of the virus. It’s becoming increasingly clear that wearing a mask is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of COVID-19. But whether or not people are willing to wear one has less to do with the risk of the pandemic than their political affiliation and their inherent belief or distrust in science.
Social media: Social media is an indispensable lifeline for people to connect to friends, families, classmates, and co-workers. This is also a potential problem; false claims or narratives about COVID-19 appealing to people’s bias or denial of science, have gone global and are spreading almost as fast as the virus itself.
While experts give some credit to companies like Facebook and Twitter for their efforts to stem the spread of coronavirus misinformation, the reality is that platforms built on engagement will often end up as platforms to spread conspiracy content, which tends to be the online information most influential and most shared. A review by the Reuters Institute of 225 pieces of COVID-19 misinformation spread by political figures and celebrities made up only 20% of the sample but accounted for 69% of engagement.
The “infodemic” seems to be most acute on Facebook, where 80 per cent of Canadian users responded in the Ryerson University survey that they encounter COVID-19 misinformation “sometimes” or more frequently. But while Facebook users were more likely to encounter misinformation, Ryerson researcher Anatoliy Gruzd said misinformation is platform-agnostic: “Misinformation can start as a post on Facebook, morph into an image on Instagram, and then become a part of a YouTube video.”


ACE responds to the infodemic
During the current COVID-19 outbreak, patients living with arthritis and at high risk of infection and largely confined to their homes have many concerns and questions and are desperately trying to get the latest, credible information about COVID-19 and what it means for them from their peers online and from web searches.
Faced with a sea of conflicting information, ACE and other patient groups, health care professional associations and public health experts have played an active role in combatting the infodemic.
ACE launched its Arthritis at Home program that makes it possible for people living with arthritis to watch or listen to video interviews with Canadian experts in clinical rheumatology, arthritis scientists, physio and occupational therapists, psychologists and health economists.
“ACE members have been telling us daily how stressed-out and even fearful they are about COVID-19. ACE believes COVID-19 will have a lasting effect on how patients living with arthritis will educate themselves with accurate, timely, fact-based information that is easily accessible. Written words can never be replaced to share arthritis facts and news but being able to see and hear directly from experts is more important than ever,” said Cheryl Koehn, ACE’s President.
The next challenge for science in the context of the coronavirus is whether the infodemic causes a significant portion of the North American public to opt-out of a future COVID-19 vaccine. The anti-vaccine movement is significant in Canada and the US.
Statistics Canada reported in July 2020 that even if there was a COVID-19 vaccine, 12% of Canadians wouldn’t take it, according to a recent questionnaire. In a CNN poll in May 2020, a third of Americans said they would not try to get vaccinated against COVID-19.
If those percentages hold or rise, public health experts warn a vaccine would be “unlikely” to provide “herd immunity,” which occurs when a sufficient proportion of a population is immune to an infectious disease, either through prior illness or vaccination, so that spread from person to person is unlikely.
While the pandemic wasn’t human-made, the infodemic surely is. But that means governments, public health authorities, patient groups, healthcare professional organizations, employers and the public itself can put a halt to it with the right strategy. And it starts with a trust not a denial in science.
Lifestyle Tips from our Arthritis at Home Experts
Research has found that one of the most important self-management techniques for people living with arthritis is regular physical activity. Exercise helps to manage pain and inflammation and also helps improve joint strength and mobility. On our Arthritis At Home program, Dr. Jasmin Ma, Dr. Jackie Whittaker and Dr. Linda Li provide helpful exercise advice for people living with arthritis. Below are some key takeaways. Remember to talk to your physiotherapist, rheumatologist or another healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program.
Tips and tricks for physical activity:
Staying Nourished During the Pandemic
Research has also emphasized the importance of eating a healthy and balanced diet for both inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis. However, eating a healthy and balanced diet can be particularly challenging during COVID-19. Luckily, Cristina Montoya, Registered Dietitian, has some helpful tips for keeping your body nourished while staying safe during the pandemic:
Listening to you
We hope you find this information of use. Please tell us what you think by writing to us or emailing us at feedback@jointhealth.org. Through your ongoing and active participation, ACE can make its work more relevant to all Canadians living with arthritis.
Update your email or postal address
Please let us know of any changes by contacting ACE at feedback@jointhealth.org. This will ensure that you continue to receive your free email or print copy of JointHealth™ insight.
Arthritis Consumer Experts (ACE)
Who We Are
Arthritis Consumer Experts (ACE) operates as a non-profit and provides free research based education and information to Canadians with arthritis. We help (em)power people living with all forms of arthritis to take control of their disease and to take action in healthcare and research decision making. ACE activities are guided by its members and led by people with arthritis, scientific and medical experts on the ACE Advisory Board. To learn more about ACE, visit www.jointhealth.org
Disclosures
Over the past 12 months, ACE received grants- in-aid from: Arthritis Research Canada, Amgen Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Canadian Rheumatology Association, Eli Lilly Canada, Hoffman-La Roche Canada Ltd., Knowledge Translation Canada, Merck Canada, Novartis Canada, Pfizer Canada, Sandoz Canada, Sanofi Canada, St. Paul’s Hospital (Vancouver), UCB Canada, and the University of British Columbia.
ACE also received unsolicited donations from its community members (people with arthritis) across Canada.
ACE thanks funders for their support to help the nearly 6 million Canadians living with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and the many other forms of the disease.
Disclaimer
The material contained on this website is provided for general information only. This website should not be relied on to suggest a course of treatment for a particular individual or as a substitute for consultation with qualified health professionals who are familiar with your individual medical needs. Should you have any healthcare related questions, you should contact your physician. You should never disregard medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this or any website.
This site may provide links to other Internet sites only for the convenience of World Wide Web users. ACE is not responsible for the availability or content of these external sites, nor does ACE endorse, warrant or guarantee the products, services or information described or offered at these other Internet sites.
Although the information presented on this website is believed to be accurate at the time it is posted, this website could include inaccuracies, typographical errors or out-of-date information. This website may be changed at any time without prior notice.

In this issue of JointHealth™ insight, Arthritis Consumer Experts (ACE) covers what you need to know about the ‘infodemic’, how we got here and what it means for arthritis patients and researchers. As an additional bonus section, we also provide some fun and helpful lifestyle tips shared by experts on our Arthritis At Home program. Afterall, even during a pandemic, people living with arthritis want to make the most of their summer and keep their joints as happy and healthy as possible!
 According to WHO, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, the phenomenon of an “infodemic” has escalated to a level that requires a coordinated response. WHO defines an infodemic as “an overabundance of information, some accurate and some not—that makes it hard for people to find trustworthy sources and reliable guidance when they need it.” Even when people have access to high-quality information, misinformation continues to spread further and faster and adds complexity to a public health emergency response.
According to WHO, in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, the phenomenon of an “infodemic” has escalated to a level that requires a coordinated response. WHO defines an infodemic as “an overabundance of information, some accurate and some not—that makes it hard for people to find trustworthy sources and reliable guidance when they need it.” Even when people have access to high-quality information, misinformation continues to spread further and faster and adds complexity to a public health emergency response.

How did we get here?
What we have learned over the past five months is that the traditional media and, even more importantly, high-powered social media have accelerated the spread of lies and the political polarization that motivates people to believe misinformation. Experts are concerned that unless the public health sphere can effectively counter misinformation, not even an effective vaccine may be enough to end the pandemic.
While fake news is anything but new, the difference is the infodemic can make people sick and even kill them if they don’t understand what precautions to take.
Beyond its effect on individuals, the infodemic erodes trust in science and government leadership at the moment when that trust is most needed. A study by the Reuters Institute found 39% of English-language misinformation assessed between January and March included false claims about the actions or policies of authorities.
The infodemic has spread nearly as widely as the pandemic itself in North America. Based on an online survey by Ryerson University researchers, misinformation about the COVID-19 pandemic is reaching a majority of Canadians who use social media and popular apps. Nearly 7 in 10 Canadians who responded to the survey said they had personally encountered misinformation about the global health crisis on social media platforms or on popular aggregator websites like Reddit.
In the US, 38% of Americans surveyed by Pew in June said that compared to the first couple of weeks of the pandemic, they found it harder to identify what was true and what was false about the virus.
An evolving outbreak: Misinformation and disinformation have always been a destabilizing feature of infectious disease outbreaks. But several factors have made the situation worse with COVID-19.
COVID-19 is new, and as scientists have learned more about the virus, they’ve had to change recommendations based on new evidence and science. That’s how science works but for people who are distrustful of health authorities, an expert changing a guideline or recommendation in a matter of days or weeks just confirms their bias and unfounded suspicions about public health recommendations.
The use of masks is an excellent example. Back in February, North American health authorities were not recommending wearing masks; by May, based on real-world evidence from countries who effectively flattened the curve, our authorities began recommending the use of masks in public places where physical distancing was difficult to maintain. Today, people are still arguing about wearing masks—a tiny infringement of personal freedoms that represents one of the few hopes of easing the spread of the virus. It’s becoming increasingly clear that wearing a mask is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of COVID-19. But whether or not people are willing to wear one has less to do with the risk of the pandemic than their political affiliation and their inherent belief or distrust in science.

Social media: Social media is an indispensable lifeline for people to connect to friends, families, classmates, and co-workers. This is also a potential problem; false claims or narratives about COVID-19 appealing to people’s bias or denial of science, have gone global and are spreading almost as fast as the virus itself.
While experts give some credit to companies like Facebook and Twitter for their efforts to stem the spread of coronavirus misinformation, the reality is that platforms built on engagement will often end up as platforms to spread conspiracy content, which tends to be the online information most influential and most shared. A review by the Reuters Institute of 225 pieces of COVID-19 misinformation spread by political figures and celebrities made up only 20% of the sample but accounted for 69% of engagement.
The “infodemic” seems to be most acute on Facebook, where 80 per cent of Canadian users responded in the Ryerson University survey that they encounter COVID-19 misinformation “sometimes” or more frequently. But while Facebook users were more likely to encounter misinformation, Ryerson researcher Anatoliy Gruzd said misinformation is platform-agnostic: “Misinformation can start as a post on Facebook, morph into an image on Instagram, and then become a part of a YouTube video.”

|
Respecting and promoting science: what it means for the Canadian arthritis community Underlying the “infodemic” is a distrust and denial of science. In Canada, we have followed the science and evidence more effectively than our neighbours in the US and have made heroes of Dr. Bonnie Henry and Dr. Theresa Tam unlike the US experience where Dr. Anthony Fauci requires 24-hour personal security from law enforcement. However, that doesn’t mean that we are immune to science denial or distrust. Science research funding from the federal government has ebbed and flowed the past 20 years often reflecting the government of the day’s trust and promotion of science. How does this historical, fluctuating lack of government support for science and research affect the Canadian arthritis community? First, some facts. Sixty per cent of the nearly 6 million Canadians with arthritis are under the age of 65 and more Canadians are affected by arthritis than diabetes, heart disease, or cancer. As the leading cause of work disability in Canada, arthritis costs the Canadian economy approximately $33 billion due to the direct costs (e.g., hospital care, physician visits, rehabilitation, prescription drugs) and the indirect costs (e.g., absence from work and lost potential earnings, underperformance at work). While the prevalence and economic burden of arthritis continue to grow, arthritis research is underfunded when compared to other disease research. The Canadian Institutes of Health Research has flattened spending on arthritis-related research over the past 15 years. For comparison, diabetes research received three times as much funding per person with diabetes; cancer research received 32 times as much funding per person with cancer. |

|
Why arthritis research is important for us Currently, during the pandemic, researchers are gathering COVID data specific to rheumatology patients that will provide important insights on how COVID-19 impacts rheumatology patients and how autoimmune diseases and immunosuppressive medications influence the risk of infection and the outcomes of COVID-19. On a broader scale, as arthritis patients and consumers, we still are living without a cure for arthritis. Government funding for arthritis research provides support to Canadian scientists and research teams who are working to learn more about arthritis and understand the experiences of people living with the disease. Some of the topics researchers are trying to discover and understand include:
|

ACE responds to the infodemic
During the current COVID-19 outbreak, patients living with arthritis and at high risk of infection and largely confined to their homes have many concerns and questions and are desperately trying to get the latest, credible information about COVID-19 and what it means for them from their peers online and from web searches.
Faced with a sea of conflicting information, ACE and other patient groups, health care professional associations and public health experts have played an active role in combatting the infodemic.
ACE launched its Arthritis at Home program that makes it possible for people living with arthritis to watch or listen to video interviews with Canadian experts in clinical rheumatology, arthritis scientists, physio and occupational therapists, psychologists and health economists.
“ACE members have been telling us daily how stressed-out and even fearful they are about COVID-19. ACE believes COVID-19 will have a lasting effect on how patients living with arthritis will educate themselves with accurate, timely, fact-based information that is easily accessible. Written words can never be replaced to share arthritis facts and news but being able to see and hear directly from experts is more important than ever,” said Cheryl Koehn, ACE’s President.
The next challenge for science in the context of the coronavirus is whether the infodemic causes a significant portion of the North American public to opt-out of a future COVID-19 vaccine. The anti-vaccine movement is significant in Canada and the US.
Statistics Canada reported in July 2020 that even if there was a COVID-19 vaccine, 12% of Canadians wouldn’t take it, according to a recent questionnaire. In a CNN poll in May 2020, a third of Americans said they would not try to get vaccinated against COVID-19.
If those percentages hold or rise, public health experts warn a vaccine would be “unlikely” to provide “herd immunity,” which occurs when a sufficient proportion of a population is immune to an infectious disease, either through prior illness or vaccination, so that spread from person to person is unlikely.
While the pandemic wasn’t human-made, the infodemic surely is. But that means governments, public health authorities, patient groups, healthcare professional organizations, employers and the public itself can put a halt to it with the right strategy. And it starts with a trust not a denial in science.

Lifestyle Tips from our Arthritis at Home Experts
Research has found that one of the most important self-management techniques for people living with arthritis is regular physical activity. Exercise helps to manage pain and inflammation and also helps improve joint strength and mobility. On our Arthritis At Home program, Dr. Jasmin Ma, Dr. Jackie Whittaker and Dr. Linda Li provide helpful exercise advice for people living with arthritis. Below are some key takeaways. Remember to talk to your physiotherapist, rheumatologist or another healthcare provider before starting a new exercise program.
Tips and tricks for physical activity:
- Dr. Jackie Whittaker reminds patients to evaluate their body before starting exercise. If your pain is 5 or lower on a scale of 10 - with 10 being the worst pain and 0 being no pain - then it is okay to start exercising. However, if your pain is over 5, you may want to consider postponing exercise for another day.
- Dr. Linda Li emphasizes the importance of moving often throughout the day, whether living with arthritis or not. Consider setting a soft reminder (such as a vibration) on your phone, computer or watch that reminds you to get up and walk around every hour. This feature may already be offered by your Fitbit or other types of activity trackers if you have one. 250 steps per hour is the most common recommendation provided by experts.
- During the pandemic, you may not have access to your regular gym and workout equipment. Dr. Jasmin Ma suggests using canned food as weights if you do not have your own weights at home. You can also wrap a towel around your ‘modified weights’ if the grip is too small and hurting your hand joints.
- If you are looking for a fun new exercise routine, check out Dr. Jasmin Ma’s 15 minute ‘exercise snacks’. There are 4 episodes in this special series, each focusing on a different set of exercises that can be done easily at home and modified to fit your level of flexibility or strength.
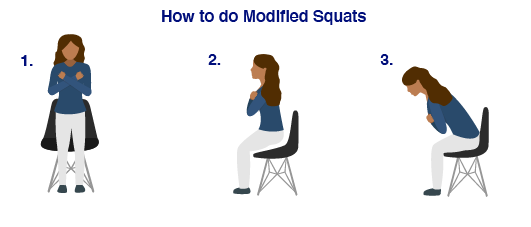
Try out these modified squats demonstrated by Dr. Jackie Whittaker for strengthening your lower extremities (knees and hips):
|
Staying Nourished During the Pandemic
Research has also emphasized the importance of eating a healthy and balanced diet for both inflammatory arthritis and osteoarthritis. However, eating a healthy and balanced diet can be particularly challenging during COVID-19. Luckily, Cristina Montoya, Registered Dietitian, has some helpful tips for keeping your body nourished while staying safe during the pandemic:
- Make your grocery list on a piece of paper (not your phone!) and throw out the list after you exit the store. This will ensure that you do not bring germs from the grocery store home with you. You can even consider leaving your phone at home or putting it in a closed pocket so that you do not inadvertently touch it while you are at the store.
- Clean foods with hard surfaces even if you do not eat the outside. For example, oranges, avocados, watermelons. Etc are often foods that we don’t wash because we are only eating the inside of them. However, when cutting them, our knives actually bring germs on the outer skin all the way through its insides.
- Consider buying frozen vegetables – they will last longer than fresh veggies meaning less trips to the grocery store, while still providing the same nutrients. They are also often less expensive and pre-cut which is a huge advantage for folks with pain or swelling in their hands.
- Great protein options with long shelf lives include eggs, canned tuna or salmon, beans and legumes.
Listening to you
We hope you find this information of use. Please tell us what you think by writing to us or emailing us at feedback@jointhealth.org. Through your ongoing and active participation, ACE can make its work more relevant to all Canadians living with arthritis.
Update your email or postal address
Please let us know of any changes by contacting ACE at feedback@jointhealth.org. This will ensure that you continue to receive your free email or print copy of JointHealth™ insight.
Arthritis Consumer Experts (ACE)
Who We Are
Arthritis Consumer Experts (ACE) operates as a non-profit and provides free research based education and information to Canadians with arthritis. We help (em)power people living with all forms of arthritis to take control of their disease and to take action in healthcare and research decision making. ACE activities are guided by its members and led by people with arthritis, scientific and medical experts on the ACE Advisory Board. To learn more about ACE, visit www.jointhealth.org
Disclosures
Over the past 12 months, ACE received grants- in-aid from: Arthritis Research Canada, Amgen Canada, Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Canadian Rheumatology Association, Eli Lilly Canada, Hoffman-La Roche Canada Ltd., Knowledge Translation Canada, Merck Canada, Novartis Canada, Pfizer Canada, Sandoz Canada, Sanofi Canada, St. Paul’s Hospital (Vancouver), UCB Canada, and the University of British Columbia.
ACE also received unsolicited donations from its community members (people with arthritis) across Canada.
ACE thanks funders for their support to help the nearly 6 million Canadians living with osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis and the many other forms of the disease.
Disclaimer
The material contained on this website is provided for general information only. This website should not be relied on to suggest a course of treatment for a particular individual or as a substitute for consultation with qualified health professionals who are familiar with your individual medical needs. Should you have any healthcare related questions, you should contact your physician. You should never disregard medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this or any website.
This site may provide links to other Internet sites only for the convenience of World Wide Web users. ACE is not responsible for the availability or content of these external sites, nor does ACE endorse, warrant or guarantee the products, services or information described or offered at these other Internet sites.
Although the information presented on this website is believed to be accurate at the time it is posted, this website could include inaccuracies, typographical errors or out-of-date information. This website may be changed at any time without prior notice.